AGYA Members
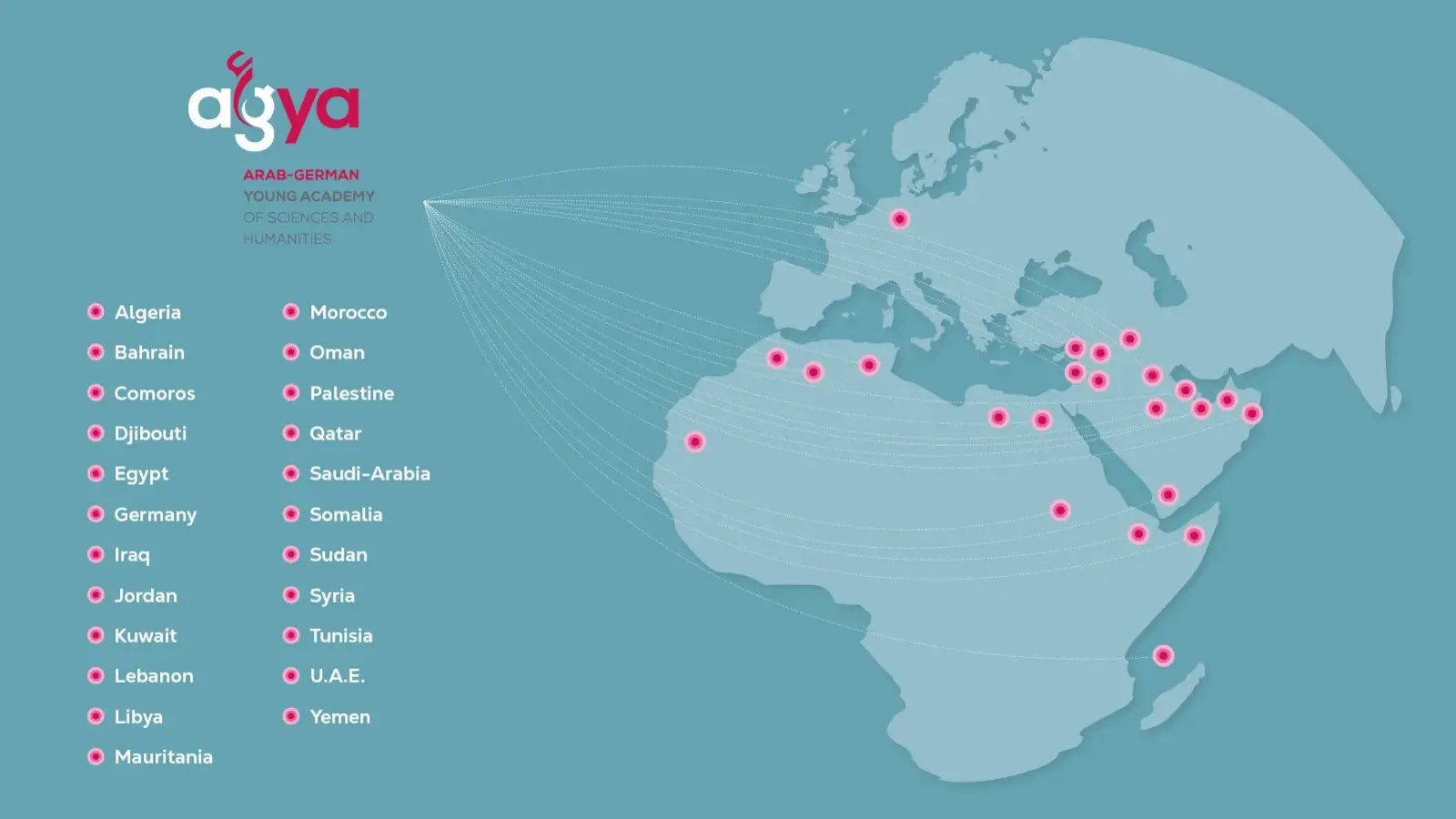
AGYA members are excellent early-career researchers from a great variety of disciplines. Half of the members are based in Germany and half in Arab countries.
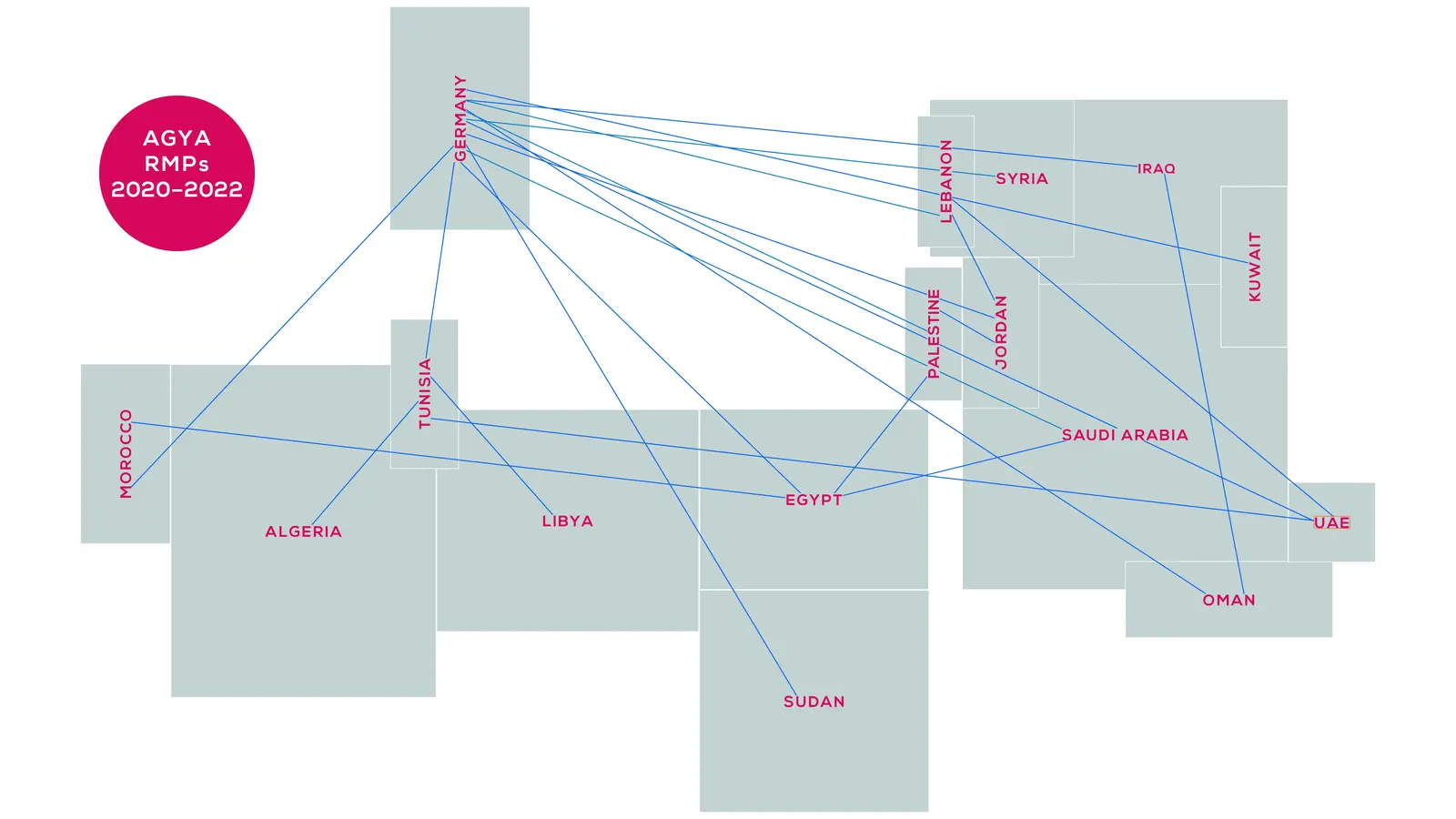
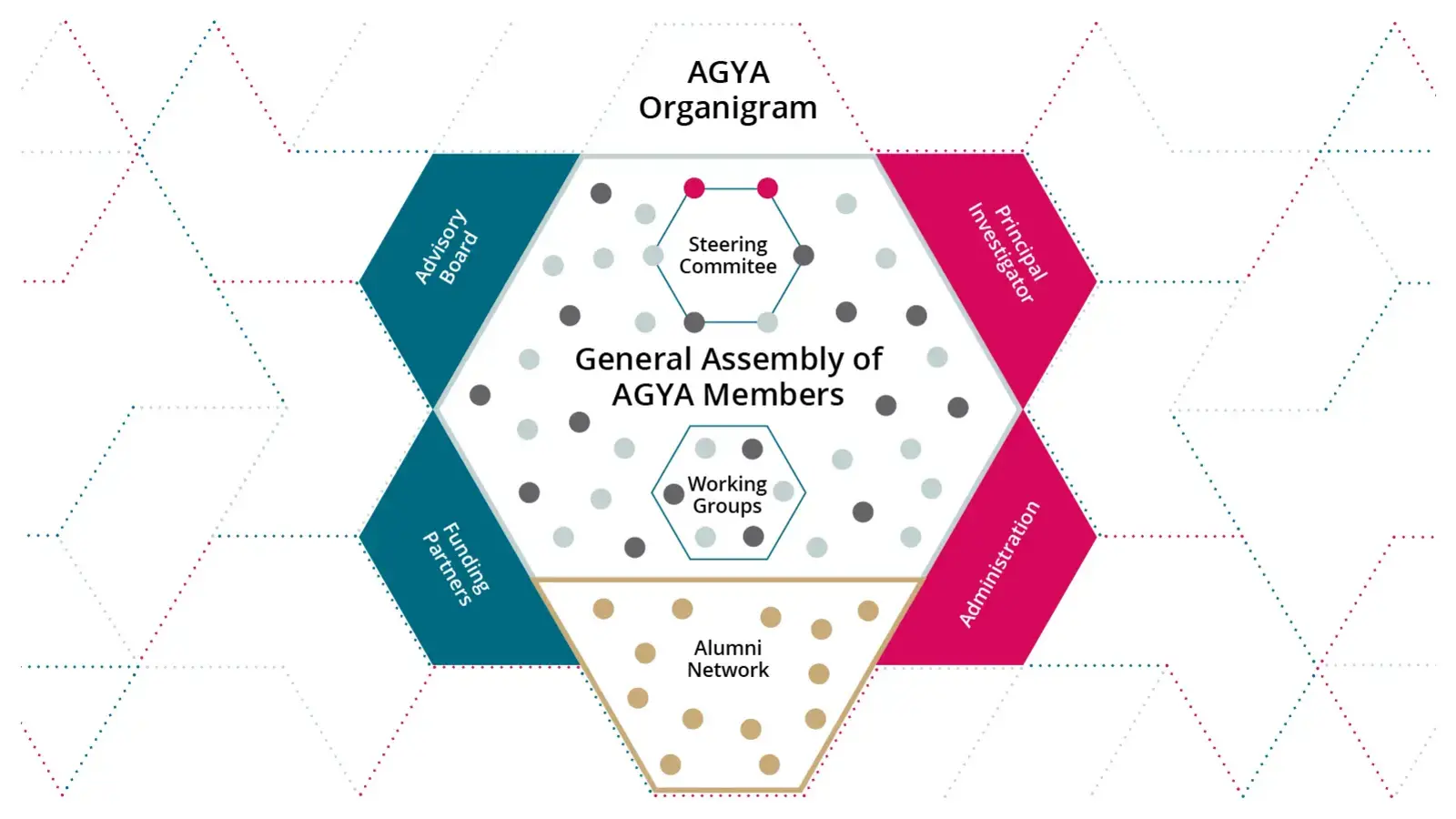
AGYA offers its 60 members the unique opportunity to develop and implement their ideas, visions, and projects within the framework of Arab-German research collaboration.
AGYA Connects Excellence in Research
How can we preserve cultural artifacts? How do young academics in Arab countries and Germany think about social robots in health care and domestic work? Find out more about the Arab-German Young Academy of Sciences and Humanities and the interdisciplinary collaborative research projects of the AGYA members!